Jul 20, 2022
What Is Supervised Learning? A Beginner’s Guide
Machine learning has reshaped how we solve real-world problems—from medical diagnoses to personalized shopping experiences. At the heart of many of these innovations lies supervised learning, a foundational approach that teaches machines through examples. If you’re just starting your journey in AI or data science, understanding supervised learning is a must. In this guide, we’ll explain what supervised learning is, how it works, types of problems it solves, and where it’s used in the real world.
Whether you're launching a DeFi platform, a supply chain solution, or a tokenized real estate venture, leveraging smart contract development services can ensure your blockchain project is secure, efficient, and future-ready.
What Is Supervised Learning?
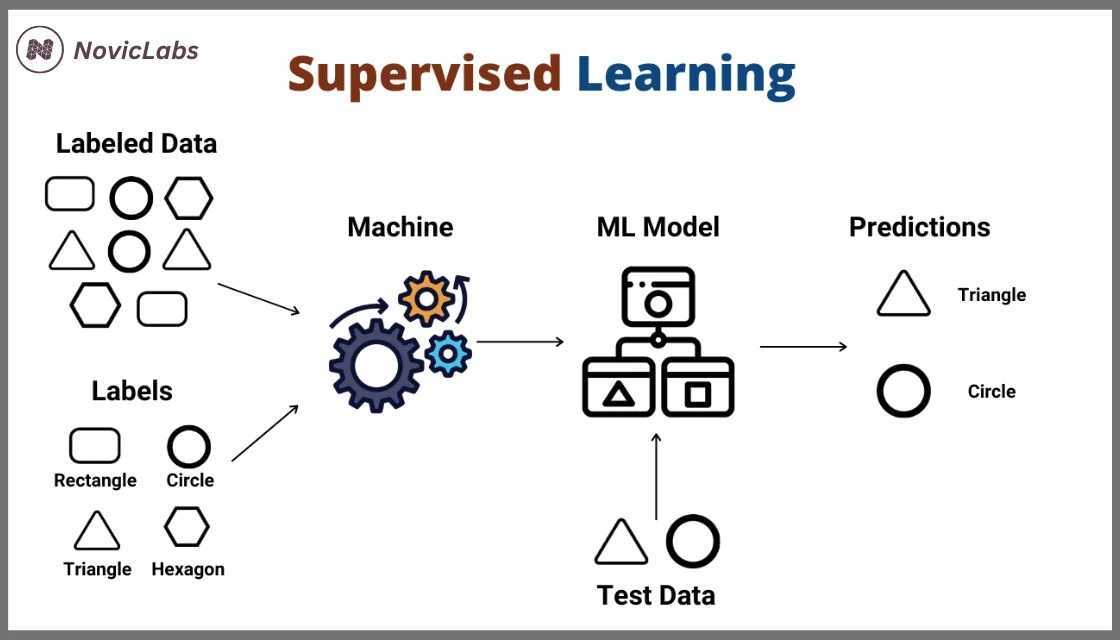
Supervised learning is a method in machine learning where the algorithm learns from a dataset that includes both inputs and their correct outputs. In essence, it’s similar to teaching a student using flashcards—each one shows a question (input) on one side and the answer (output) on the other.
The algorithm studies these pairs to understand the link between input and output, allowing it to make accurate predictions when given new inputs.
How Supervised Learning Works (Step-by-Step)
Collecting Data:
You start with a dataset that includes input features (like age, income, or pixel values in an image) and the correct labels (like approved or rejected for a loan application).
Training the Model:
The algorithm examines the data to identify patterns or relationships between the input features and their corresponding labels.
Model Testing:
You test the trained model using new data it hasn't seen before to check how well it performs.
Making Predictions:
Once validated, the model is ready to predict outcomes for future or unknown data.
Two Main Types of Supervised Learning
Classification
This is used when the outputs are categories.
Examples:
Email classification: Spam or Not Spam
Medical diagnosis: Disease A, B, or C
Image recognition: Dog, Cat, or Bird
Regression
This is used when the output is a continuous value.
Examples:
Predicting house prices
Estimating a car’s fuel efficiency
Forecasting monthly sales
Popular Supervised Learning Algorithms
Decision Trees: Break down data into branches based on feature values.
Linear Regression: Captures and models the relationship between input variables and a continuous output variable.
Logistic Regression: Best for binary classification tasks.
Support Vector Machines (SVM): Good for clear-cut classification problems.
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN): Assigns a class to a data point based on the majority class of its nearest neighbors in the training set.
Random Forest: An ensemble method that combines multiple decision trees, where each tree contributes a vote to determine the final prediction.
Real-World Applications of Supervised Learning
Healthcare: Predicting the likelihood of diseases based on patient data.
Finance: Detecting fraud in banking transactions.
Marketing: Predicting customer behavior or churn rates.
Retail: Recommending products based on purchase history.
Agriculture: Identifying crop diseases using labeled images.
Benefits of Supervised Learnin
High Accuracy: When provided with quality data, supervised learning models can make very accurate predictions.
Well-Defined Goals: Because we use labeled data, the learning objective is clear.
Final Thoughts
Supervised learning is a key technique in machine learning that empowers machines to learn from labeled examples, allowing them to make accurate predictions and informed decisions. Whether you're building a recommendation engine or developing a diagnostic tool, supervised learning offers a structured and efficient way to teach machines how to learn from the past and predict the future.
Understanding supervised learning not only helps you grasp the basics of AI but also opens doors to building smarter, data-driven applications. As more industries turn to AI, knowing how supervised learning works will give you a clear advantage in the tech-driven world.
STREAMLINE YOUR BUSINESS WITH AI?
Main
Resources
Developers
Company
Contact Us
+1 (999) 888-77-66
hello@noviclabs.com
Location
483920, Indonesia,
Lampung 22/2/5, Office 4
© 2023 Noviclabs All rights reserved.