Jul 20, 2022
Hashing in Blockchain: A Complete Guide
Hashing in Blockchain is a fundamental process used to secure data and ensure integrity across the distributed ledger. A hash is a fixed-size alphanumeric string generated by a mathematical algorithm that transforms input data of any length into a unique identifier. This transformation ensures that even the smallest change in the input will drastically change the output hash — making it virtually impossible to reverse-engineer the original data.
From securing transaction data to maintaining the structure of blocks, hashing is essential in maintaining Blockchain’s transparency and immutability.
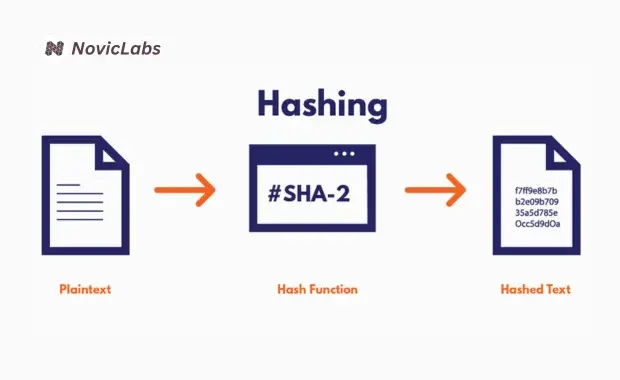
How Hashing Works in Blockchain
Hashing works by taking input data—like a transaction or block information — and running it through a cryptographic hash function, such as SHA-256 (used in Bitcoin). This function produces a distinct, fixed-length string known as the hash or digest.
Key properties:
Deterministic: A given input will always generate the exact same hash value.
Irreversible: It’s computationally infeasible to reconstruct the original input from its hash.
Collision-resistant: It’s extremely unlikely that two distinct inputs will result in the same hash output.
This process ensures each block in the chain is tightly connected and tamper-proof.
Why Hashing is Important in Blockchain
Hashing plays several vital roles in Blockchain systems:
Data Integrity: Hashing helps verify that data remains unchanged during transmission or storage.
Security: Hashes help secure the Blockchain by preventing unauthorized modifications.
Block Linking: Each block contains the hash of the previous block, forming a secure chain.
Efficient Verification: Hashes enable quick data validation without the need to inspect the entire content.
Popular Hashing Algorithms in Blockchain
Here are some commonly used hashing algorithms:
SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256)
Used in Bitcoin and other Blockchain systems, SHA-256 produces a 256-bit hash and is known for its security and reliability.
Keccak-256 (used in Ethereum)
Designed for Ethereum, Keccak-256 is a part of the SHA-3 family. It is optimized for Blockchain" class="active:font-bold">smart contracts and fast transaction processing.
Scrypt & X11
These are used in alternative cryptocurrencies like Litecoin and Dash, offering resistance against ASIC miners.
Use Cases of Hashing in Blockchain
Hashing goes beyond mining. Some other applications include:
Digital Signatures: Used to verify identity and authenticity of transactions.
Merkle Trees: Hashing allows for quick and secure verification of data in large blockchains.
Blockchain" class="active:font-bold">smart contracts: Ethereum uses hashing for storing and referencing contract states.
Token Integrity: Ensures token supply and balances can’t be tampered with.
Challenges and Considerations
Hash Collisions: While rare, two inputs producing the same hash would be a major issue.
Computational Cost: Especially in PoW, hashing requires significant computational power.
Quantum Threat: Future quantum computing might undermine current hash algorithms, leading to a shift to quantum-resistant methods.
Conclusion
Hashing plays a vital role in Blockchain by providing reliability, transparency, and immutability—key elements that establish trust in the technology. From securing blocks and verifying transactions to enabling mining and digital signatures, hashing is the silent hero that powers decentralized networks.
As Blockchain technology evolves, hashing will continue to play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of digital systems — making it a must-know concept for developers, investors, and enthusiasts alike.
STREAMLINE YOUR BUSINESS WITH AI?
Main
Resources
Developers
Company
Contact Us
+1 (999) 888-77-66
hello@noviclabs.com
Location
483920, Indonesia,
Lampung 22/2/5, Office 4
© 2023 Noviclabs All rights reserved.